In the landscape of modern manufacturing, two processes often come under the spotlight due to their widespread applications and significance in producing high-precision components: spring manufacturing and CNC turning. Both processes serve distinct purposes and involve unique methodologies, yet they are crucial in their respective domains. This article delves into the intricacies of spring manufacturing and CNC turning, exploring their methodologies, applications, advantages, and challenges.
Understanding Spring Manufacturing
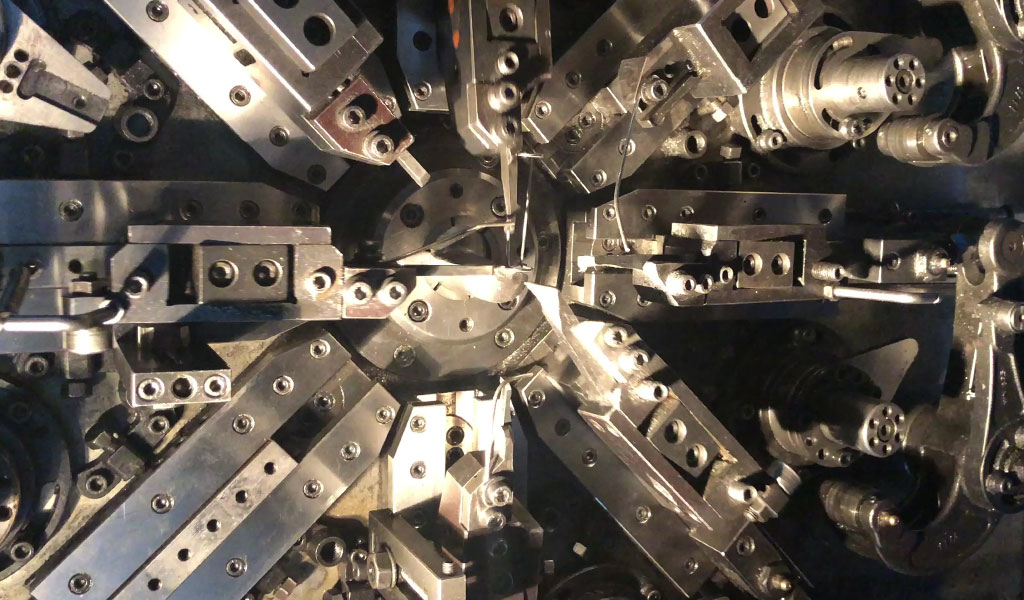
Spring manufacturing involves creating various types of springs, such as compression springs, extension springs, torsion springs, and wire forms. The process begins with selecting the appropriate material, commonly high-carbon steel, stainless steel, or non-ferrous alloys. The chosen material is then wound into the desired shape and size using a coiling machine. After coiling, the springs undergo heat treatment to enhance their strength and durability. Additional processes such as grinding, shot peening, and coating may be applied to meet specific requirements.
Types of Springs
- Compression Springs: These springs are designed to operate with a compressive load, providing resistance when compressed. They are widely used in automotive, aerospace, and industrial applications.
- Extension Springs: Unlike compression springs, extension springs are loaded in tension, meaning they extend when a load is applied. They are commonly used in applications such as trampolines, garage doors, and farm machinery.
- Torsion Springs: These springs operate by twisting and exerting torque in opposite directions. They are often found in clipboards, mousetraps, and various automotive components.
- Wire Forms: These are custom-shaped wire products used in a range of applications, including electrical contacts, clips, and various industrial machinery components.
Advantages of Spring Manufacturing
- Versatility: Springs can be manufactured in a wide range of sizes and shapes to meet diverse application needs.
- Durability: Properly manufactured springs are highly durable and can withstand significant stress and strain.
- Cost-Effective: Spring manufacturing can be cost-effective, especially for large production runs.
Challenges in Spring Manufacturing
- Precision: Achieving precise dimensions and mechanical properties can be challenging, especially for complex spring designs.
- Material Selection: Choosing the right material for specific applications is crucial to ensure performance and longevity.
Understanding CNC Turning
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) turning is a machining process used to create cylindrical parts by removing material from a rotating workpiece using cutting tools.
The process is controlled by a computer program that dictates the movement and operation of the lathe.
CNC turning is known for its ability to produce high-precision components with intricate details.
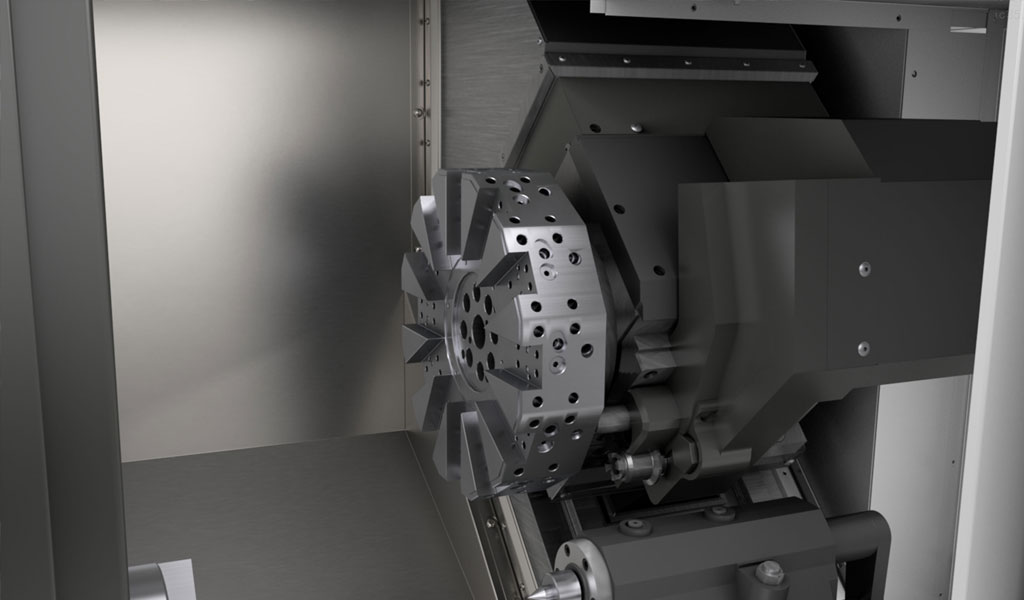
CNC turning is widely used in various industries, including aerospace, automotive, medical, and electronics, to manufacture components such as shafts, bushings, pulleys, and intricate housings. The process is ideal for producing both prototypes and high-volume production runs.
Advantages of CNC Turning
- Precision and Accuracy: CNC turning machines can achieve extremely tight tolerances, ensuring high precision and accuracy in the final product.
- Efficiency: The automated nature of CNC turning allows for efficient production, reducing lead times and labor costs.
- Consistency: CNC turning ensures consistent quality across large production runs, minimizing variations and defects.
- Complex Geometries: The technology enables the creation of complex geometries and intricate designs that would be challenging to achieve with manual machining.
Challenges in CNC Turning
- Initial Setup Cost: The initial investment in CNC machinery and software can be high, making it a significant consideration for small businesses.
- Programming Complexity: Creating accurate CNC programs requires skilled operators and programmers, adding to the operational complexity.
- Material Limitations: While CNC turning can work with a variety of materials, some materials may pose challenges due to their hardness or brittleness.
Similarities and Differences Between Spring Manufacturing and CNC Turning
Spring manufacturing and CNC turning are two distinct manufacturing processes that play crucial roles in producing components for various industries. While they serve different purposes and employ different techniques, they share some similarities and exhibit differences in their methodologies, applications, and advantages. Let’s explore these aspects in detail:
Similarities:
- Precision Engineering: Both processes require precision engineering to produce components with tight tolerances and accurate dimensions. Whether it’s creating intricate spring designs or machining complex cylindrical parts, precision is essential for ensuring the functionality and performance of the final products.
- Material Selection: In both processes, the selection of materials is critical to achieving desired mechanical properties and performance characteristics. Whether it’s choosing the right alloy for a spring or selecting the appropriate metal for CNC turning, material selection plays a crucial role in determining the suitability and durability of the final components.
- Quality Control: Both processes involve rigorous quality control measures to ensure that the manufactured components meet the required specifications and standards. From material testing to dimensional inspections, quality control ensures that defects are minimized, and the finished products meet customer expectations.
- Technological Advancements: Advances in technology have significantly impacted both spring manufacturing and CNC turning processes. From automated coiling machines and CNC lathes to sophisticated software for design and programming, technological advancements have improved efficiency, accuracy, and productivity in both manufacturing processes.
Differences:
- Purpose and Functionality: The primary difference between spring manufacturing and CNC turning lies in their purpose and functionality. Spring manufacturing is focused on creating components that store and release mechanical energy, providing resilience and flexibility in various applications. In contrast, CNC turning is geared towards machining cylindrical parts with intricate geometries and precise dimensions, serving different functional requirements.
- Methodology: Spring manufacturing involves coiling wire into specific shapes and sizes, followed by heat treatment and other secondary processes to achieve desired mechanical properties. CNC turning, on the other hand, utilizes computer-controlled cutting tools to remove material from a rotating workpiece, shaping it into the desired form. While both processes involve machining operations, their methodologies and techniques differ significantly.
- Applications: Spring manufacturing finds applications in a wide range of industries, including automotive, aerospace, electronics, and consumer goods, where springs are used for various purposes such as suspension, damping, and actuation. CNC turning, on the other hand, is commonly employed in industries such as automotive, aerospace, medical, and electronics to produce components like shafts, bushings, connectors, and housings.
- Complexity and Customization: While both processes offer customization options, CNC turning generally allows for greater complexity and intricacy in part design due to its ability to machine intricate geometries and features with high precision. Spring manufacturing, while versatile, may have limitations in producing highly complex shapes and features compared to CNC turning.
- Material Flexibility: CNC turning offers greater flexibility in terms of material compatibility, allowing for machining of metals, plastics, and composites with relative ease. Spring manufacturing, while adaptable to various materials, may be more specialized depending on the specific requirements and performance characteristics of the spring.
In summary, while spring manufacturing and CNC turning share similarities in terms of precision engineering, material selection, quality control, and technological advancements, they differ significantly in their purpose, methodology, applications, complexity, and material flexibility. Understanding these differences is crucial for manufacturers to choose the most appropriate process for their specific needs and requirements, whether it’s producing resilient springs for automotive suspension systems or machining intricate components for aerospace applications. Ultimately, both processes play vital roles in modern manufacturing, driving innovation and advancement across diverse industries.
In Conclusion
Spring manufacturing and CNC turning serve different purposes. Spring manufacturing focuses on producing components that store and release energy, providing mechanical force in various applications. CNC turning, on the other hand, is a subtractive machining process aimed at creating precise cylindrical parts by removing material.
Spring manufacturing and CNC turning are two essential manufacturing processes with distinct methodologies, applications, and advantages. Spring manufacturing is vital for producing components that store and release energy, playing a crucial role in various mechanical systems. CNC turning, with its precision and versatility, is indispensable for creating high-precision cylindrical parts across multiple industries.
Understanding the strengths and challenges of each process can help manufacturers make informed decisions based on their specific needs and production requirements. Whether the goal is to produce durable springs or intricate cylindrical components, both spring manufacturing and CNC turning offer valuable solutions in the realm of modern manufacturing.
Flexibility and Customization
Both processes offer a high degree of flexibility and customization. Spring manufacturing allows for the creation of a wide range of spring types and shapes tailored to specific needs. CNC turning excels in producing components with intricate details and complex geometries, offering customization options through precise programming.
Production Volume
Spring manufacturing can be cost-effective for large production runs, particularly when producing standard spring designs. CNC turning is suitable for both low and high-volume production, with its efficiency and automation making it a viable option for producing large quantities of parts with consistent quality.
Material Considerations
In spring manufacturing, the choice of material is critical to ensure the spring’s performance and longevity. High-carbon steel, stainless steel, and non-ferrous alloys are commonly used. CNC turning, however, can work with a broader range of materials, including metals, plastics, and composites, providing greater flexibility in material selection.
Technological Requirements
CNC turning requires significant technological investment, including high-precision machinery and sophisticated software. Spring manufacturing, while also reliant on specialized machinery, may have lower technological entry barriers, particularly for simpler spring designs.